Bird Pyramid Safety. The Safety Triangle diverts attention away from the most serious incidents that could lead to deaths the Campbell Institute said. Heinrichs Law relies on the assumption that the number of reported accidents is inversely proportional to their severity.
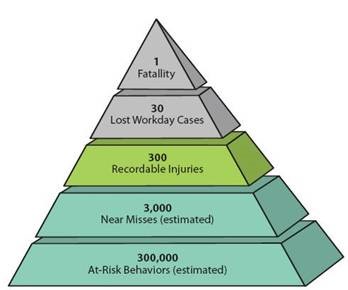
A Scientific Approach Heinrich 1931 was based on the analysis of accident data collected by his employer a large insurance company. The safety pyramid represents the claim that for every workplace accident that causes a major injury there are 29 that cause minor injuries and 300 accidents or near misses that cause no injuries. The above is a typical pyramid or triangular representation of the theory.
The safety pyramid represents the claim that for every workplace accident that causes a major injury there are 29 that cause minor injuries and 300 accidents or near misses that cause no injuries.
Occupational safety and health specialists study past work-related illnesses and injuries to understand how to prevent future ones. These studies are often combined to form what is called the safety triangle or the safety pyramid. On this assumption. Years after Heinrich put forward the pyramid Frank E Bird developed it into the accident triangle commonly seen today.